Pre-Implementation Best Practices
Credit and A/R projects are large, complex, expensive and fraught with risks. This e-book demystifies technologies such as Robotic Process Automation and Artificial Intelligence to help finance leaders transform operations.
Pre-Implementation Best Practices
Credit and Accounts Receivable (A/R) Process Assessment
A credit and A/R process assessment is the first step in the pre-implementation phase. A common pitfall with most firms is that the project leaders straight away get into requirements analysis without understanding the status quo of credit and A/R processes within their organization. To achieve success, it is of utmost importance to determine the current state to set the foundation for future change. The assessment process provides clarity on the following three items:
- The scope of the receivables transformation project
- Budget and timelines
- Resources required
The assessment process improves decision-making that will have a direct impact on the scope, the cost and the value capture of the project.
Receivables Project Core Team Selection
As a first step, set-up a core team comprised of A/R process owners, IT, senior execs and end users. It is also strongly recommended to add 3rd party consultants to challenge the ?it is how things have always been done? mentality.  The core team should be chartered to review the current processes and systems to evaluate the value capture of implementing receivables automation. Figure1 highlights the team composition.
The core team should be chartered to review the current processes and systems to evaluate the value capture of implementing receivables automation. Figure1 highlights the team composition.
Credit and A/R Assessment Process
At its core, the assessment process provides a detailed view of the activities that that each team member is responsible for and also help track the KPIs of the project?s implementation. Figure 2 outlines the five stages in the audit process below: 
Process Re-Engineering
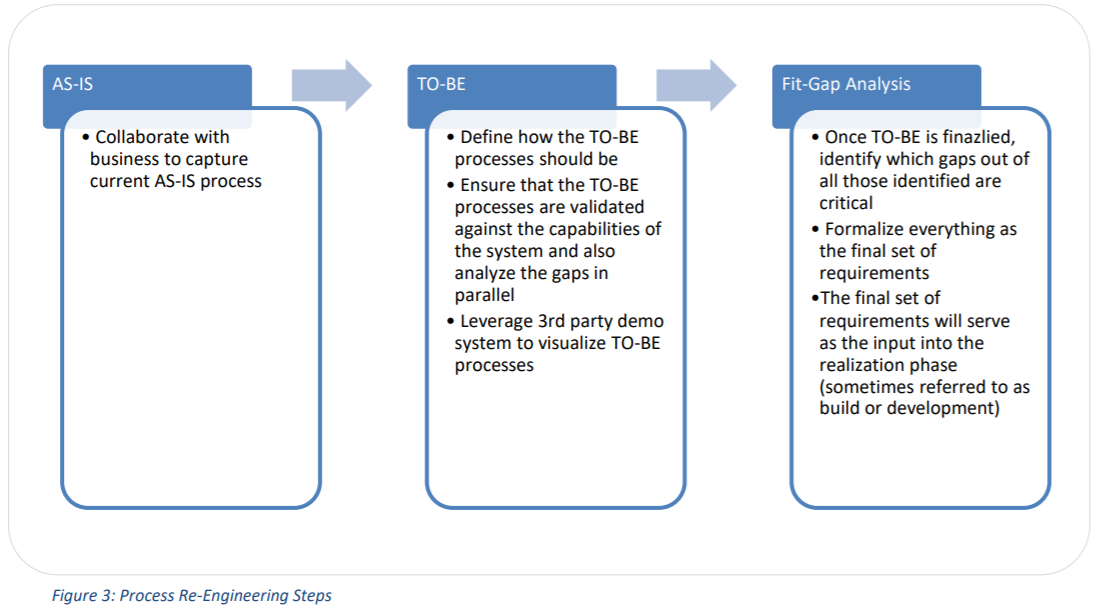
Technologies such as Robotic Process Automation open up new opportunities to gain efficiencies in routine processes. Therefore, it becomes critical for business teams to ?unlearn? or at least shed biases WRT the AS- IS process/legacy systems. Any attempt to design a ?new? system for an ?old? process might at best bring in marginal improvements in operational performance whereas redesigning the processes and taking advantage of the emerging technologies is imperative to achieving significant performance improvements. To avoid making this common misstep, follow the outline below:
- Identify Key AS-IS Processes: Start with identifying key processes that directly impact the bottom line of the organization. Study the AS-IS processes without trying to solve all the problems of the current system. For example, a HighRadius client, Dr Pepper Snapple Group, used a Lean 6-Sigma tool called Gemba to observe and analyze the Credit and A/R processes. To learn more, watch this video.
- Determine TO-BE Processes: Once the AS-IS processes have been analyzed, design the TO-BE processes. The TO-BE processes need to take into consideration the IT system that supports these processes. Employ a demo system to visualize how these proposed processes would work in the software to help the core team identify the gaps in their current system.
- Conduct a Fit-Gap Analysis: Most receivables technology implementations are customized according to the business needs. Once the gaps have been identified, the core team must prioritize the gaps according to the criticality and the impact on the bottom-line to define the scope of the project.
Fit-Gap Analysis Document
The fit-gap analysis document should ideally have the following fields:
| Requirement†description Business†Priority | ROI†Priority Category Minor†Gap | Major†Gap ERP†Gap Solution†Options |
 ?ROI Priority? is a key column as it is important to track what impacts the KPIs. The below graph (Figure 51) is a good representation of the type of KPIs that could be used to track the performance of credit and A/R teams.
?ROI Priority? is a key column as it is important to track what impacts the KPIs. The below graph (Figure 51) is a good representation of the type of KPIs that could be used to track the performance of credit and A/R teams.  Other important metrics and reports to consider include the following:
Other important metrics and reports to consider include the following: 
Return on Investment/Cost-Benefit Analysis
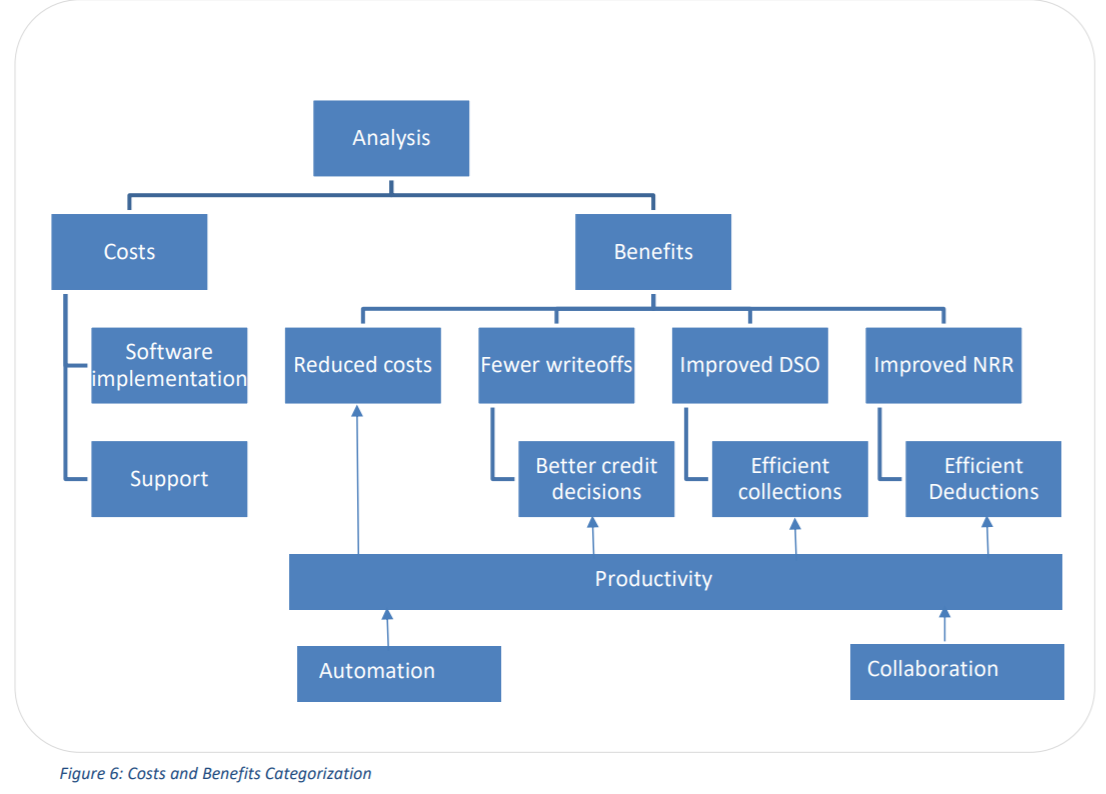
Implementing a credit, A/R and invoicing solution directly impacts the costs of a company. Putting together a business case involves a thorough review of the current processes and systems in place and identifies opportunities for improvement via process re-engineering and automation. Some of the KPIs and metrics listed could directly impact the bottom line. For a more in-depth understanding, please read the eBook on Automating Accounts Receivable- Building a Winning Business Case that outlines the cost-benefit analysis. Figure 6 analyzes the costs vs benefits to make a business case for receivables transformation projects: