Building an Ideal Tech Stack for Real-Time Visibility into Customer Performance
Insights from Uber, The Hackett Group and more on building the ideal tech stack for real-time visibility into customer performance.
What Do Most GBS Leaders Find Challenging Today
Today, most global business services (GBS) leaders are working with their teams towards meeting the CFO’s goals of safeguarding cash flow and optimizing working capital. The task becomes significantly harder when GBS models operate in silos.
The major reason for these silos is the lack of a centralized system across diverse business units. Decentralization of these global units also leads to challenges like:
1. The inability to collaborate with internal teams –
GBS teams working with decentralized systems across different locations cannot collaborate with other teams to evaluate the root cause, resulting in a poor customer experience in the long run.
2. The inability to deliver on SLAs –
A/R teams in most GBS models are involved in manual and transactional tasks, which prevents them from taking up roles that require strategic decision-making skills. Hence, most GPOs are forced to rethink their SLAs (service level agreements) because their A/R teams cannot deliver the desired objectives on time. This results in a negative impact on working capital.
3. The inability to compete with the best-in-class in the industry –
Every GPO’s goal is global expansion to thrive in their industry. But the price of expansion is that they must deal with competition in the market. Some GBS leaders believe that staying local will help them avoid competition, but they are continuously tasked with leveling up to be at par with their peers.
It is significantly more challenging if they continue to operate on a legacy platform/For example – legacy-based ERP applications when their peers have invested in advanced automation capabilities.
4. The inability to implement innovative GBS models –
To stand out from the competition in the industry, every GBS organization must try to deploy innovative operational models for their operations successfully.
But it is often challenging for these leaders to implement such models. One of the primary reasons is that most finance executives are doubtful about the success of the operational model, and getting their buy-in is comparatively quite difficult.
The above challenges point to the lack of end-to-end visibility in GBS models. GBS leaders need to look for ways to implement a more harmonious mode of operation to meet the CFO’s objectives.
Why Having a 360-Degree View Over GBS Is Critical to Driving Revenue Growth
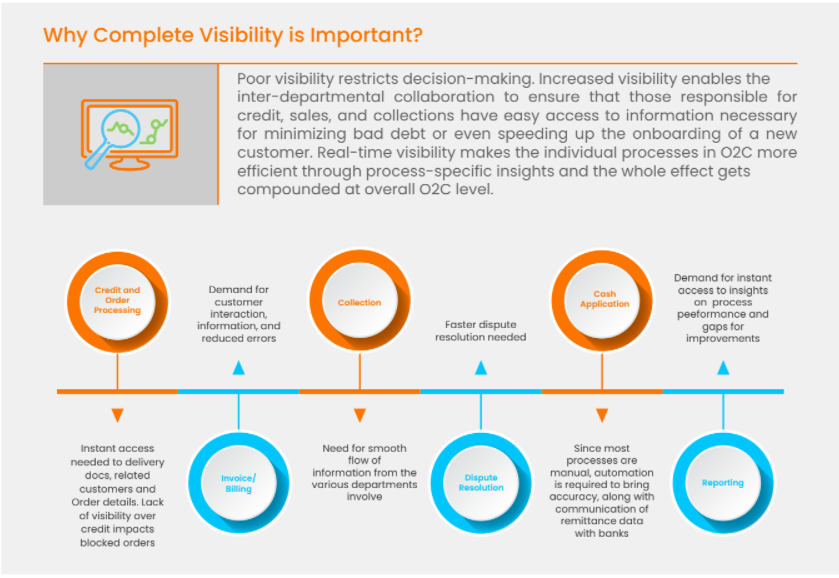
Visibility is a key metric that distinguishes a best-in-class O2C process from the rest. Poor visibility can often lead to errors, information silos, and delays in cash conversion.
For instance, teams like credit and sales that crave robust communication and regular data exchange will most likely make less accurate decisions without centralized visibility.
Decision-makers such as CFOs/CXOs constantly seek visibility across key A/R performance metrics like day sales outstanding (DSO) to generate actionable insights for the core business.
Homer Smith from Uber highlights –
- Analyzing information manually from different lines of business is a time-consuming process as it requires data sourcing, normalizing, and consolidating information.
- It impacts the 360-degree view of customers because manually processing information requires bandwidth. This reduces the time to analyze the information and make strategic business decisions.
Tammy Lindorf from Martin Marietta highlights –
- Analyzing information manually from different lines of business is a time-consuming process as it requires data sourcing, normalizing, and consolidating information.
- It impacts the 360-degree view of customers because manually processing information requires bandwidth. This reduces the time to analyze the information and make strategic business decisions.
Moustapha Ould Ibn Mogdad from Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS) highlights –
Now, with a focus on cash application, the hit rate has reached 98%.
- Visibility is required on the entire credit model. BMS looks for agility, speed, and efficiency from invoicing, cash application, credit management, and risk management processes.
- The credit model requires an overview of customers to evaluate their creditworthiness.
- A working cash application model and an inactive credit evaluation system will provide an incomplete picture of customers and result in inaccuracies in decision-making.
Why Do GBS Operations Need a 360-Degree View into Customer Behavior
Customers form the front and center of every A/R operation, and every GBS model is executed with this into consideration. There are three main reasons why GBS teams should adopt 360-degree visibility into customer behavior trends:
- Enhance Customer Experience: Complete visibility over customers helps the A/R team prioritize follow-ups based on payment status for past dues. For instance, following up with a customer who has already paid might lead to a negative customer experience. Therefore, collections teams should have real-time information on each customer’s credit due, which would help them prioritize defaulters.
- Improve Customer Intelligence: A/R teams could personalize the entire process and make it less prone to errors by acquiring a holistic view of customers and access to their payment behavior and preferences. For instance, invoices would be sent at the right time, and organizations would effectively communicate with customers to secure timely payments.
- Identify Customer Risk: A centralized view of the customer would enable A/R teams to assess the risk a customer poses in terms of payment delay or credit overdue. This would help leaders deprioritize low-risk customers, create targeted dunning strategies, and reallocate the resource bandwidth, to high-risk customers.
Based on insights collected from GBS leaders, we have identified five critical areas in A/R shared services that can greatly benefit from enhanced visibility:
1. Data Management:
Centralized automated systems with better visibility ensures reduction in operational silos by consolidating all the relevant information on a single platform. As a result, different teams can have access to the latest data about the customers.
Benefits-
- Getting access to the data at a single place so relevant data like sales orders, invoices, proof-of-delivery (POD) documents, packing slips, and remittances can be tracked in a central system. This eliminates the process of physically searching for information on paper.
- Integrating multiple systems across A/R enables easier and faster access to information without connecting individual ERPs.
2. Cash Management:
With enhanced visibility into receivables performance, it becomes possible for teams to make decisions that impact cash flow and help optimize working capital.
Benefits-
- Guaranteeing the availability of information on upcoming liabilities in advance and ensuring accurate cash flow projections.
- Reducing revenue leakage by enabling instant corrective action and lowering the write-off limit based on a customer’s payment behavior.
3. Time Management:
In O2C, almost one-fourth of the effort and time goes into resolving disputes that could be easily avoided with better visibility. Reduced cycle time is one of the most sought-after parameters to measure the success of A/R processes.
Benefits-
- Enabling A/R leaders to identify bottlenecks and remove process inefficiencies without any delay quickly. This is achieved through tools to track and monitor employees’ workload and time spent on processing transactions.
- Making query resolution faster by providing A/R teams with visibility on the invoices or incoming payments status.
- Integrating and normalizing data such as PO numbers, quantities, item numbers, and prices, from ERP directly. This leads to, elimination of the time-consuming manual data entry.
4. Audit and Quality Management:
Real-time visibility ensures that A/R processes are consistent, streamlined, and compliant to reduce process-wide variance and associated risks.
Benefits-
- Handling the complete audit trail seamlessly for every touchpoint invoice or payment journey and maintaining accountability and security throughout the process.
- Identifying missing documents required for audit, thereby reducing the chances of penalties.
5. Decision Management:
End-to-end visibility from an automated system also provides consolidated insights from relevant data. This enables A/R teams to make more informed decisions. Some examples include:
Benefits-
- Easier overview of transaction-related information like check images, payment remittances, and other notes and documentation.
- Faster assessment of customers’ creditworthiness, and increased frequency of periodic credit reviews with real-time access to the latest data.
This is how better visibility across receivables ensures significant business value for GBS models to drive success on multiple fronts.
What Does the Ideal Tech Stack Look Like
A GPO’s advise

Linda Lei,
GPO of Customer Payments,
Deductions, and Credit
Uber
Linda believes that ERP is at the core of the tech stack. It is required to integrate all the data processed across systems and transfer them back to the ERP system. It is essential to integrate ERP with an automated solution to manage workflows. Uber uses an in-house order management system, along with outsourced ERP systems. In addition, they also have integrated an AI-powered automated system to optimize their global A/R operations.
Thus, information pulled from the order management systems by the ERP is shared with third-party systems. For example, aging data is pulled from the ERP and shared with third-party systems to monitor the credit-risk levels and manage cash application and collections. This type of integration also helps Uber have a 360-degree view of the customer.
Managing data across a legacy ERP platform is a cumbersome task – add to that the processing of large volumes of data and it turns into a nightmare for the A/R team. Uber leverages a third-party automated solution to drive efficiency and manage the volume of data for business units that have larger A/R. Several parameters need to be analyzed and customized to provide business insights for reporting data, and the information is synchronized with its in-house or a centralized system.
Despite a clear understanding of the significance of global visibility, several large organizations run accounts receivable, accounts payables, and inventory in silos. This is due to disparate IT systems, lack of integrated tools, or M&A complexities.
While it is not easy for businesses to achieve end-to-end visibility in one go, it is possible to gradually improve the extent of visibility by considering the following when building the tech stack:
1. Integrated Platform:
- Ideally, the system should work well with the legacy ERP systems as a prerequisite for end-to-end integration of the O2C processes.
- It should be capable of easy integration with the existing ERP system and should cause minimal business disruption during the implementation phase.
2. Single Data Entry Point:
- It is important to have a single data entry point to make changes in the system, such as updating customers’ billing addresses or making corrections in invoicing that gets updated in all systems in real-time.
- It would ensure access to the latest data across teams. According to Homer, Uber is working on a self-service dashboard that could provide real-time reporting of operations and have a data integration that is updated regularly.
3. Analytics:
- The digitized and centrally stored information is valuable only if it can be analyzed to generate insights on various business aspects.
- An ideal tech stack would certainly include advanced analytics tools with predictive capabilities.
4. Reporting:
- A dynamic dashboard is needed instead of static reporting.
- With an analytical system for consuming and analyzing all the data in one go, creating reports becomes a piece of cake with the help of data-driven dashboards.
Dashboard is the one of the most important requirements in a technology stack to enable global visibility and easy decision-making.
Homer Smith,
GPO of Billing, Credit, and Collection
Uber
The above eBook was an extract from an extensive thought leadership Whitepaper titled:
“Future of Shared Service Centers for Order-to-Cash”
What You’ll Learn From this Whitepaper:
- The evolution of A/R SSCs becomes a core part of global business operations and plays a critical role in overall business decisions.
- Why AI-powered automated A/R systems are critical for digitally transforming SSCs.
- Why 84% of digital transformations fail and how visibility and tracking of business outcomes and KPIs are significant for a successful project.


